Top Climate Change Risks: Heat, Precipitation, Flood
Use this page to learn how climate change is affecting people in West Virginia.
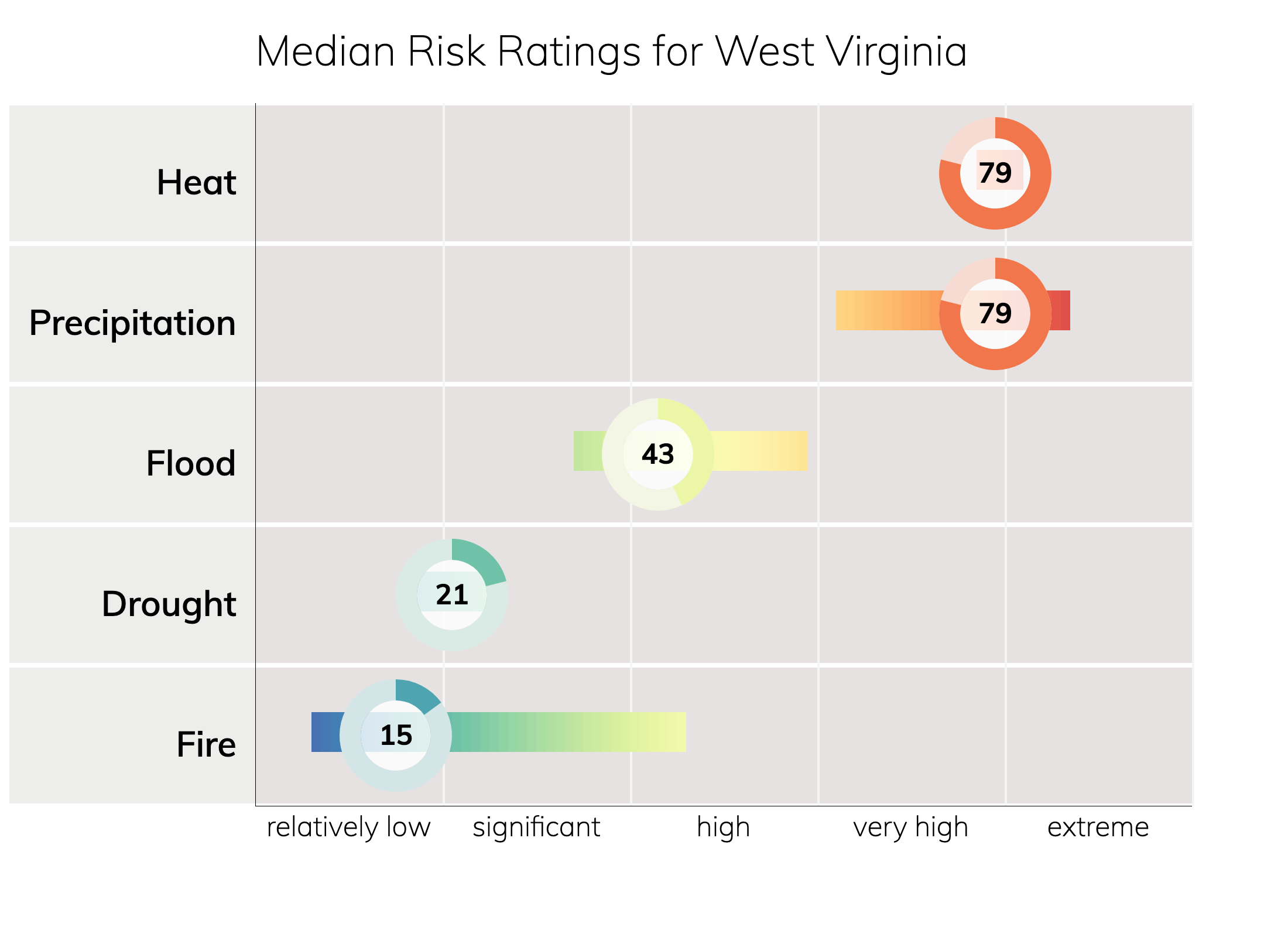
Climate Change Risk Ratings for West Virginia
People in West Virginia will experience especially increased risks from heat, precipitation, and flood due to climate change over the next 30 years. These risks, through 2050 and beyond, may change depending on how much we reduce emissions in the near future.
Get an Instant Risk Assessment
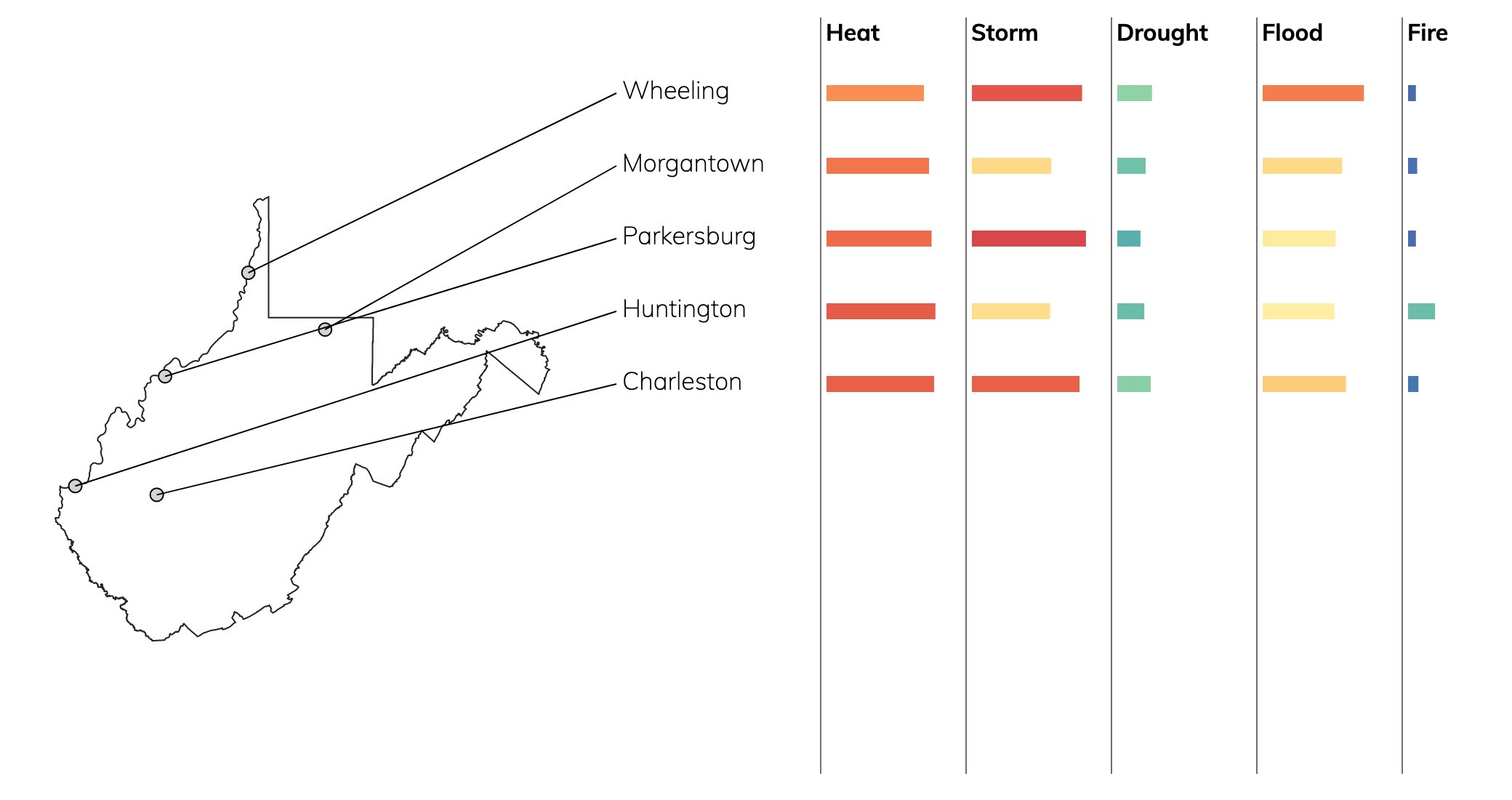
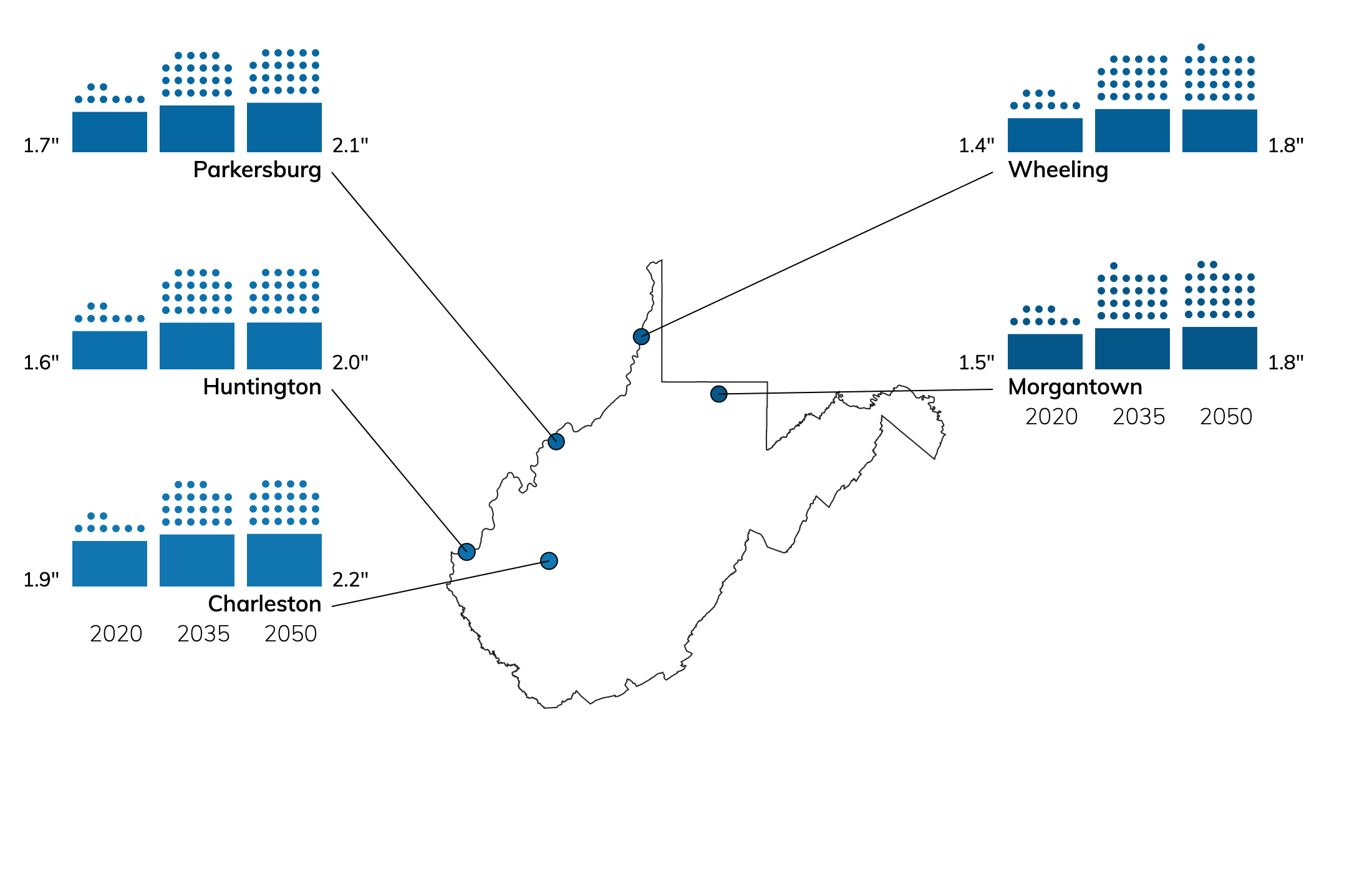
Climate Risks for Cities in West Virginia
Of these top cities in West Virginia, the city with the highest overall risk is Charleston. The city with the lowest overall risk is Wheeling.
- For heat, Wheeling has the lowest risk and Huntington has the highest risk.
- For precipitation, Huntington has the lowest risk and Parkersburg has the highest risk.
- For drought, Parkersburg has the lowest risk and Wheeling has the highest risk.
- For fire, Parkersburg has the lowest risk and Huntington has the highest risk.
- For flood, Huntington has the lowest risk and Wheeling has the highest risk.
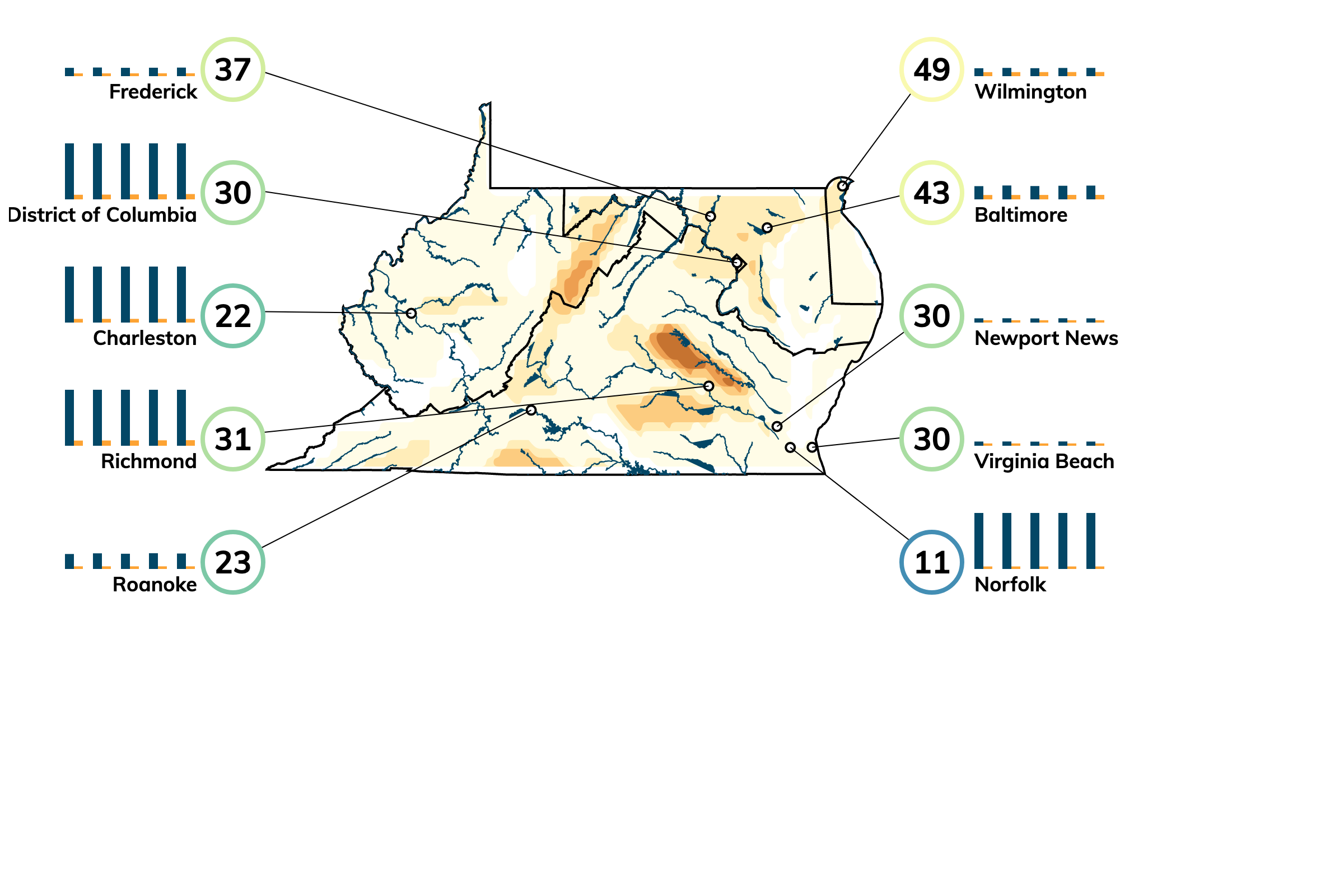
Comparing West Virginia and Other States
Among the lower 48 states, West Virginia's highest ranking is #2 for flood risk.
Arizona ranks highest for flood risk Utah and Nevada rank lowest for flood risk

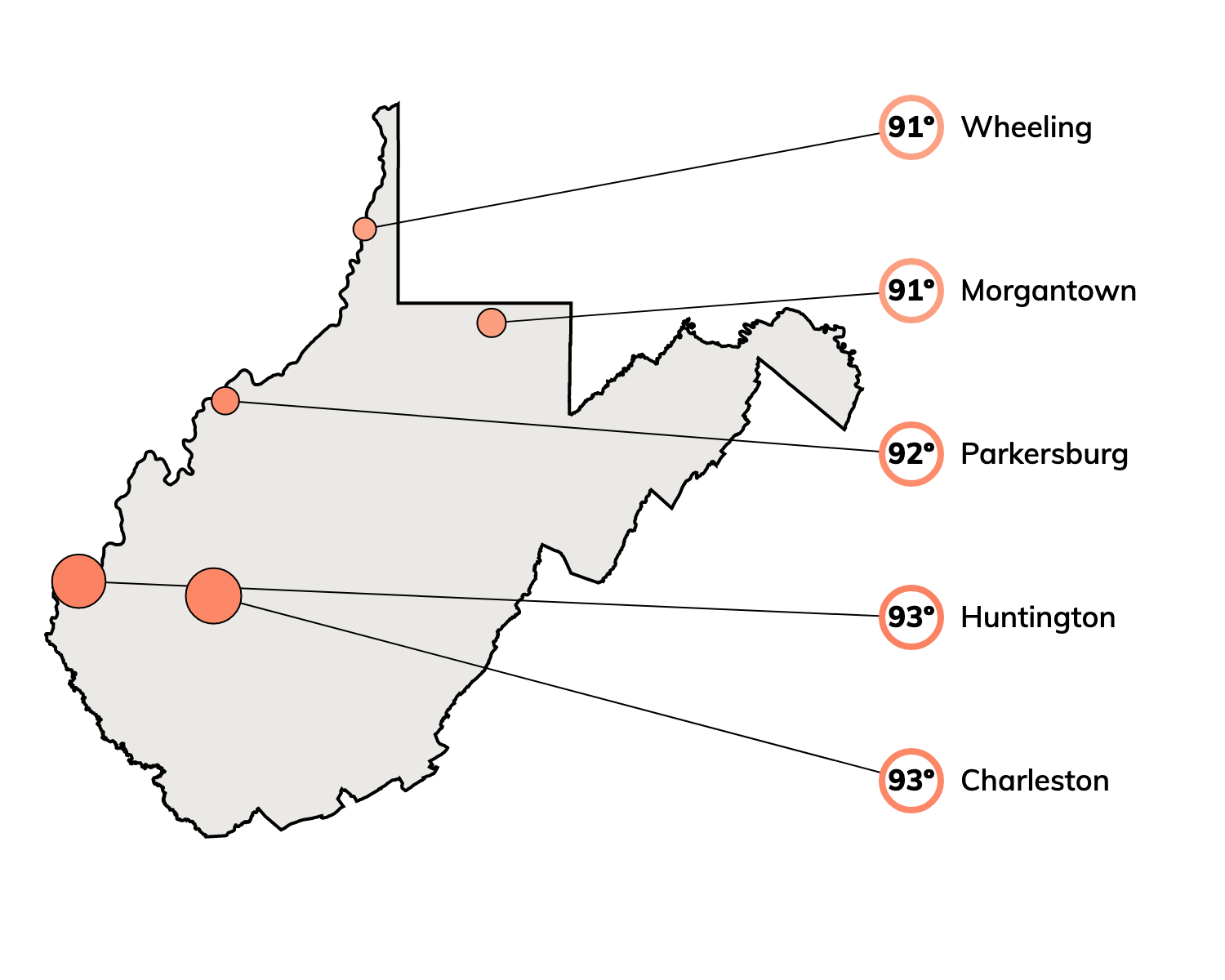
Heat Risk in West Virginia with Climate Change
An extremely hot day in West Virginia is about 91ºF. This is based on historical maximum temperatures on the top 2% of days in an average year.
The frequency of very hot days is increasing. On average, someone in West Virginia will experience about 47 extremely hot days in 2050.
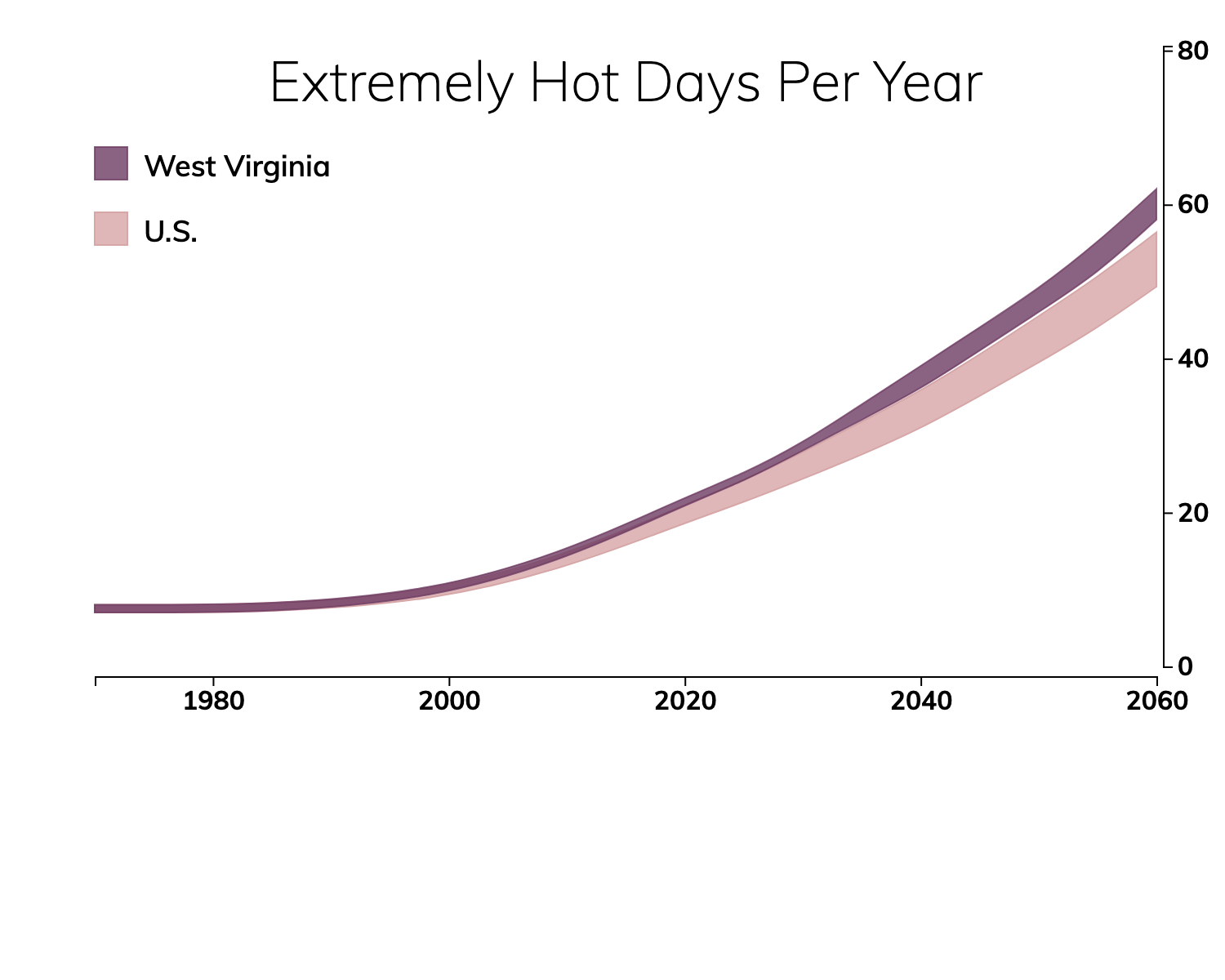
Precipitation Risk in West Virginia with Climate Change
To measure precipitation risk, we look at the amount of precipitation that falls in 48-hour periods exceeding a location-specific threshold, and how many times this happens per year. A precipitation threshold is based on the top 1% of rainiest days per year for a location.
Drought Risk in West Virginia with Climate Change
Drought risk is based on water stress, which is a projection of how much of the water supply will be taken up by human demand.
How can we prevent climate change and protect our homes and communities?
Mitigating climate change—by eliminating our emissions into the atmosphere and reducing our strain on the environment—and adapting to our changing planet are both vital to our well-being.
Understand Risks
Check your address and get a free report describing risks to your property and in your area.
Protect Homes and Communities
Check our free report for tips on protecting your home from hazards.
Find Balance